Explain the Different Types of Ion Channels
Carrier proteins transport molecules. Voltage-gated ion channels and ligand-gated ion channels are two types of gated ion channels.
In fact a majority of ion channels fall into these two broad categories.

. HVA high voltage activated Ca v 21. In the diagram 3 types of membrane potentials are shown. There is a different type of facilitated diffusion that involves channel proteins.
Different types of ion channels have been described. Less-selective channels form pores. Opening of a Na channel will cause the cell to depolarize as Na ions move into the cell ie the membrane potential.
Start studying 3 Types of Ion channels. Voltage-gated calcium ion channels are located at axon terminals. And ion channels that are dependent on G proteins.
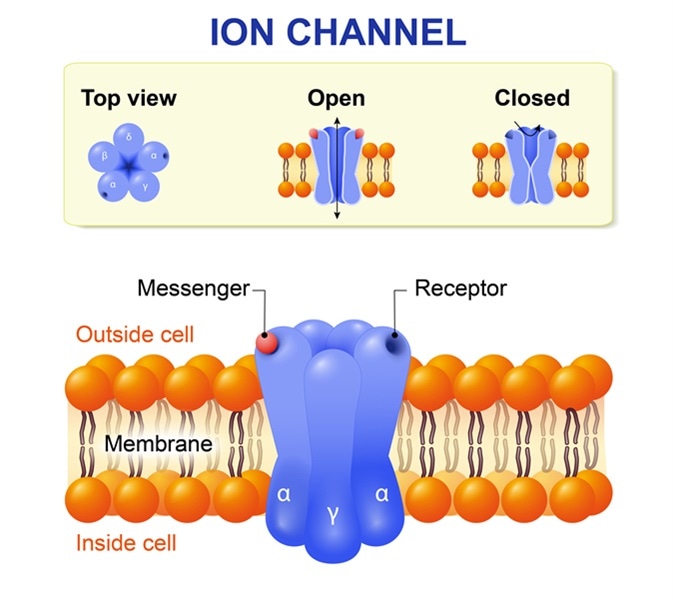
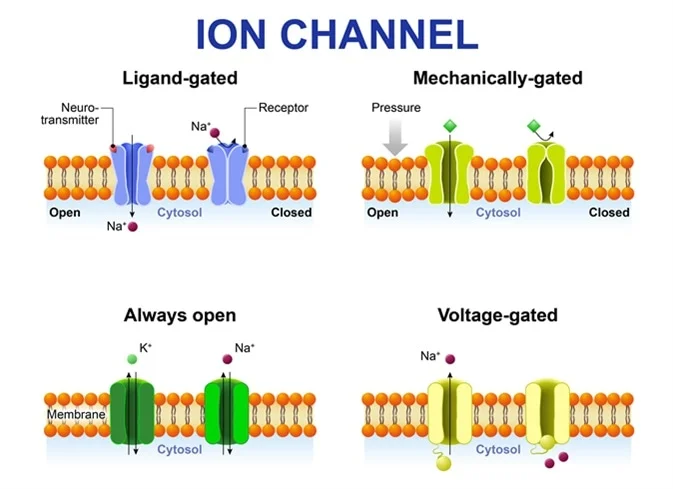
These proteins dont bind to molecules but instead they open a channel which allows smaller molecules and ions such as potassium calcium sodium and chlorine to transport quickly. The ligandgated channels that are regulated by ligands ie chemicals that bind to it. Voltage-gated ion channels are large transmembrane proteins that enable the passage of ions through their pore across the cell membrane.
There are a few polar very large molecules that are lipid-insoluble or. Sodium atom loses 1 electron to form a sodium ion Na which is cation. Channels that respond to mechanical electrical voltage-dependent ion channels or chemical stimuli ligand-gated ion channels.
Ca v 23. α 2 δ β possibly γ. Carrier proteins flip between two conformations.
Ion channels can be either non-gated or gated. α 2 δ β possibly γ. Na K Ca2 and Cl ions mostly move through ion channels.
Channel proteins contain a pore facilitating the transport of molecules. Other channel types require either three or five homologous subunits to generate the central conducting pore. Primary transporters symporters and antiporters are the three types of transporters.
Inwardly Rectifying Potassium Channels. For instance much insight into the detailed operation of ion channels has come from recent X-ray crystallographic studies of a bacterial K channel Figure 46. Voltage-gated ion channels that are selectively permeable to each of the major physiological ionsNa K Ca 2 and Cl-have now been discovered Figure 44A-DIndeed many different genes have been discovered for each type of voltage-gated ion channel.
Understanding the physical structure of ion channels is obviously the key to sorting out how they actually work. Ion channels come in many different types some of which are selective for specific types of ions such as K Na and Ca 2. These channels belong to one superfamily and carry pivotal roles such as the propagation of neuronal and muscular action potentials and the promotion of neurotransmitter secretion in synapses.
Cerebellar granule cells other neurons. Sakmann and Neher invented the patch clamp technique in 1976. Cation A positively charged ion is known as cation.
They were awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology and Medicine in 1991. Transmembrane ion channels regulate when ions can move in or out of the cell so that a precise signal is generated. This finding was unexpected because Na channels.
Gated channels or non-gated channels. The mechanically gated channels that are ion channels whose pore responds to mechanical stimuli. R-type calcium channel Residual intermediate-voltage-activated.
Ligand-gated channels activated by ACh GABA or Gly. Purkinje neurons in the cerebellum Cerebellar granule cells. A cation is formed by the loss of one or more electrons by an atom.
Common Aspects of Ion Channel Structure and Function. In a neuron chemically gated ion channels are present on the dendrites and cell body. Channel proteins are of two types.
The voltage-gated channels that are gated by changes in membrane potential. Ion Channels Ligand-Gated Channels Mechanically-Gated Channels Voltage-Gated Channels and Leak Channels. Several different types of channels work together to generate and propagate the electrical signal.
Ion channels that are controlled by phosphorylationdephosphorylation mechanisms. General reasons for facilitated diffusion. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
Ligand-gated ATP activated Cl- channels. How can V m changes be due to either the opening or the closing of ion channels. RMP is shown at 2 values.
N Review Questions n. Namely voltage gated ligand gated and stress-activated ion channels. Depending on the factor s that produce their opening and closing gating ion channels are classified into four types.
Along the axon are voltage-gated sodium ion and potassium ion channels. P-type calcium channel Purkinje Q-type calcium channel. In solution ions are stabilized by polarized water molecules in the surrounding environment.
Gated ion channels are three types. Patch-Clamp Technique which allows you to observe the functions of individual ion channel in different cell types revolutionized the study and practice of cellular biology. Voltage-gated Sodium Channels.
There are two types of ions. Sodium ion Na magnesium ion Mg 2 chloride ion Cl and oxide ion O 2. Voltage-gated ion channels ligand-gated ion channels and aquaporins are the three types of ion channels.
The entry side of both these channels normally exists as closed and they open under specific conditions only. Channel proteins are fixed. Other K selective channels with pore-forming P domains.
Channel proteins transport ions. For example 10 human Na channel genes have been identified. -70 mV and -50 mV.
This particular molecule was chosen for analysis because the large quantity of channel protein needed for. Narrow highly selective ion channels mimic the water environment by lining the conducting pore with polarized carbonyl oxygen atoms.
Types Of Ion Channels In The Body
0 Response to "Explain the Different Types of Ion Channels"
Post a Comment